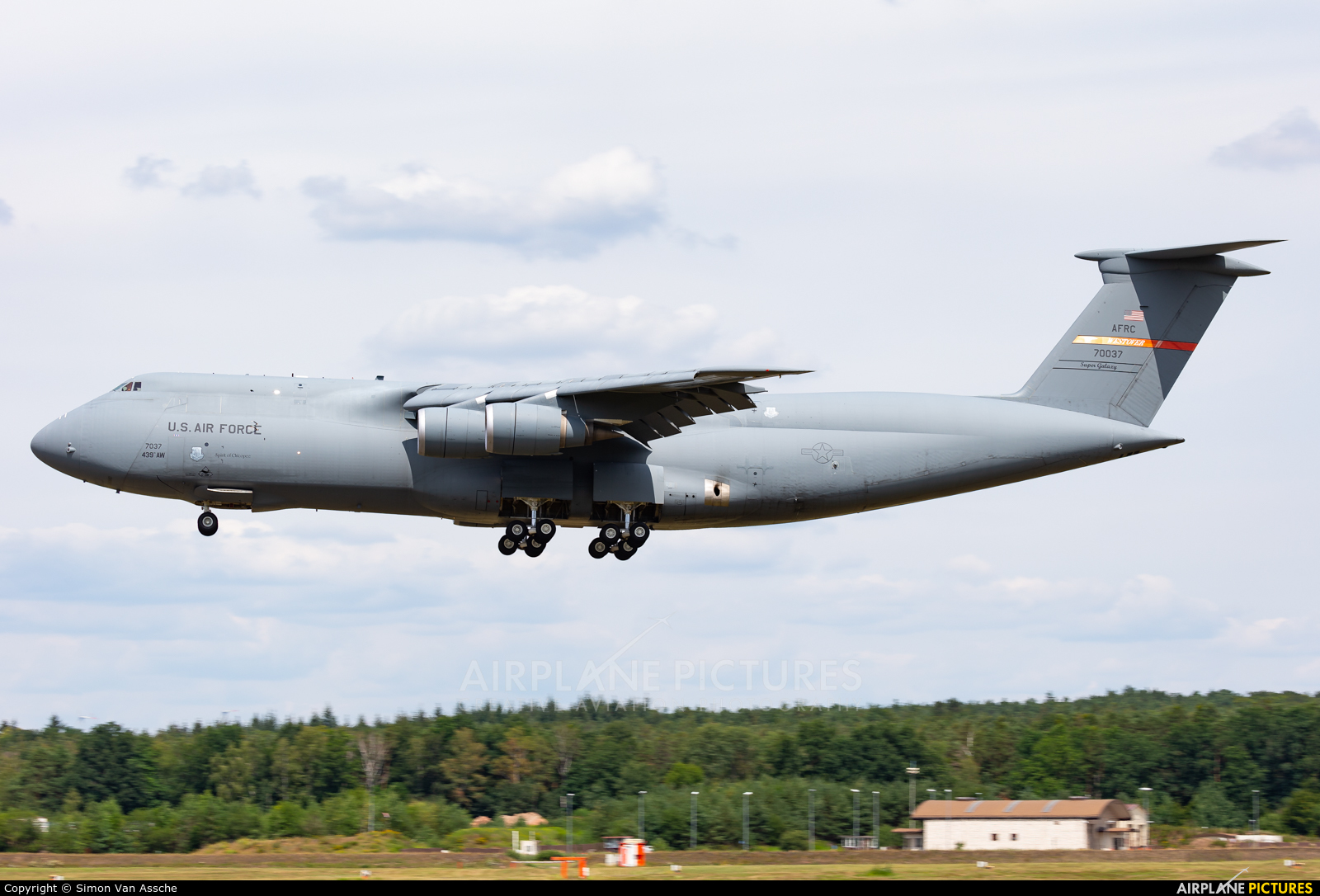
C 6 Aircraft - The C-5 modernization approach is proven. In three flights operating out of Dover AFB, Delaware, a joint U.S. Air Force and Lockheed Martin crew set 43 world aviation records, demonstrating the C-5M's ability to redefine global airlift.
In deployed airlift operations, the C-5M is demonstrating a new era of highly capable, reliable and affordable airlift. With departure reliability rates greater than 90 percent and payload increases of 20 percent over legacy C-5s, the Super Galaxy is delivering more to the warfighter on every mission.
C 6 Aircraft

With a substantial improvement in unrefueled range, the C-5M is overflying traditional en-route fuel stops, enabling a reduction in fuel consumption by as much as 20 percent. This is the OEM difference. I was told the Olympic had a steel tube inner fuse structure for the faint of heart who were beginning to prefer metal to wood.
The Original Equipment Manufacturer Oem Difference - Proven Performance
The low-wing Alcor was classic Loughead = all-wood monocoque with strength to weight ratio = mild steel verified by Richard Von Hake. The Lodestar was similar in layout to most Lockheed transport aircraft of the inter-war years.
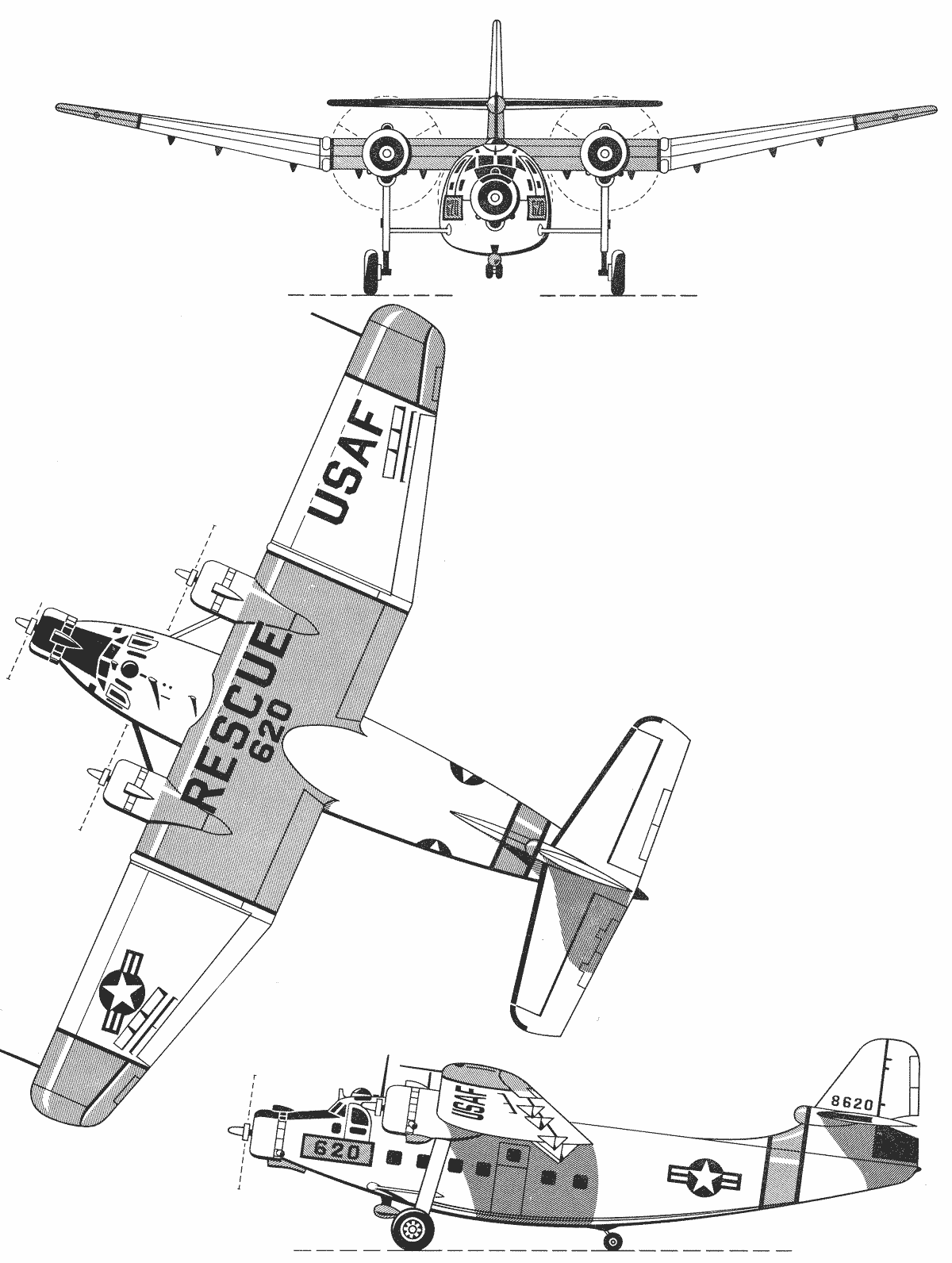
It had low mounted tapered wings, with a moderate dihedral. The fuselage had flat sides, and a rather more pointed nose than earlier models. It had a high mounted tail, with twin vertical control surfaces at the ends.
The standard version had a row of small cockpit windows on both sides, and a cabin door towards the rear of the left side of the aircraft. Their first aircraft was the Olympic Duo-4, and its fuselage was similar to the Lockheed Vega 5. In place of the Vega's single radial engine were two Menasco C4 Pirate engines.
These in-line, four-cylinder engines were air-cooled and produced 125 hp (92 kW). The engines were positioned in the nose of the Duo-4 so that the tips of the propellers cleared each other by about 3 in (76 mm).
C-/ C- / C- / C- / C- - Lockheed Model Lodestar
The engines were laid on their sides so that their heads were close together and the crankshafts were farthest apart and canted out at a slight angle. The Duo-4's engine arrangement had less air resistance than a normal twin-engine plane.
In addition, when one engine was shut down, the Duo-4 behaved much like a single-engine aircraft. Lockheed built more C-60As for the AAF (325) than any other version of the military Lodestar. Soon after the war began, the need for air evacuation was met by the peacetime practice of using regular transports.
The first occasion requiring the movement by air of large numbers of patients occurred in January 1942 during the construction of the Alcan Highway to Alaska. The second occurred in Burma in April 1942. In both instances regular transport planes (C-47s) already equipped with litter brackets were pressed into ambulance service.
In February 1937, Allan started a new aviation company: the Alcor Aircraft Corporation. The "Alcor" came from Allan Lockheed Corporation. Alcor's first official aircraft (the Duo-6 had been built before the company was formed) was the C-6-1 Junior Transport.
It was designed to carry six to eight passengers. The C-6-1 used the engine installation of the Duo but with improved C6S-4 Super Buccaneer engines that produced 275 hp (205 kW) at 2,400 rpm for takeoff.

Each engine was canted out 4 degrees and the propellers cleared each other by 12 in (0.3 m). Converted from a Super Electra, it differed primarily by having the fuselage lengthened by 1.68m to provide accommodation for 15 to 18 passengers, depending upon the other facilities provided;
some were produced with high-density bench seating for a maximum of 26 passengers, and were available with a variety of engines by Pratt & Whitney and Wright. Despite the improved economy demonstrated by the Lodestar, Lockheed failed again to achieve worthwhile sales in the United States as most operators were committed to purchasing DC-3s from the Douglas Company.
Fortunately, the type appealed more to export customers, with airlines or government agencies in Africa, Brazil, Canada, France, the Netherlands, Norway, South Africa, the UK and Venezuela ordering a total of 96 aircraft. Sources: – Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1932 by C.G.
Grey – Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1934 by C.G. Grey – Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1938 by C.G. Gray and Leonard Bridgman – Lockheed Aircraft since 1913 by Rene J. Francillon (1982/1987) – “Commercial Aviation: An American Feeder-Line Machine,” Flight 6 July 1934
– "A 'Flat' Engined Transport," Flight 12 May 1938 – http://1000aircraftphotos.com/Contributions/HornDavid/9336.htm – http://www.aerofiles.com/_al.html – Brief Allan Lockheed 1910-1942 Autobiography – http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Allan_Loughhead In October 1934, the United States placed operating restrictions on single-engine transports carrying passengers. This regulation marked a permanent shift to multi-engine transports for passenger service.
Presumably, the twin-engine Duo would have done well under the new regulations with its ability to perform like a conventional single-engine aircraft in the event of one engine being shut down. Unfortunately, the Duo-6 crashed in late 1935 and was not repaired.
The aircraft had a low-wing, and the main gear retracted back into the wing with the wheels turning 90 degrees to lay flat. The wings and fuselage had a structure made mostly of wood. However, there were some components in high-stress areas that were made of metal.
The fuselage had a circular section and was made up of laminated spruce framework with a two-piece plywood skin that was molded under pressure. The engines were closely cowled and faired into the nose and wing.
The C-6-1 was a streamlined aircraft that was very efficient and had excellent flight characteristics. The four to six passenger Duo-4 was a high-wing cantilever monoplane. The monocoque fuselage had a wooden structure and was covered with a plywood skin that was molded under pressure.
The wings also had a wooden structure and were covered with plywood. The aircraft (registered as NX962Y) was first flown by Frank Clarke in 1930. In March 1931, the Duo-4 was damaged when a sudden gust of wind caused it to nose-over and then collide with a vehicle during a landing at Muroc (
now Edwards Air Force Base), California. Unfortunately, this incident caused investors to back away from the Lockheed Brothers Aircraft Corporation, and funds were not available to quickly repair the Duo-4. Great to hear from you! I'm very glad you found the article and that it earned your stamp of approval.

And thank you very much for the great additional information. I did not know the twin recovered by itself and continued to fly; what a shame there was no one onboard to land it. There were quite a number of warplanes based on the Clarence Kelly Johnson-designed Lockheed Electra and the later Model 18 Lodestar.
The C-60 is a twin-engine transport based on the Lockheed Model 18 Lodestar, the Lockheed equivalent of the DC-3. Lockheed 10/14/18 were twin-engine monoplanes - the L 10 (Electra) carrying 10 passengers at 200 mph in 1934;
the 14 (Super Electra) carried 12 passengers at 240 mph in 1937; the 18 (Lodestar) carried 14 passengers at 225 mph in 1939. The resulting aircraft was a twin-engined, all-metal, twin-tailed, mid-wing monoplane with the main landing gear retracting into the engine nacelles.
The tail wheel did not retract. As with the Model 14, the aircraft was equipped with leading-edge slots and Fowler flaps. The trend of aircraft design is seen in the high wing loadings of 31.76 and 33.5 lb./sq.
ft. for the two loaded weights. To retain the moderate landing speed of 65 mph is only possible with the very efficient Fowler flaps. Tony Stadlman told me how Dad tricked the shell parts from the Olympic to comply with a round and larger fuse.
Tony told him you could not use the skins from 3 smaller oranges to fit over a bigger orange. Dad told him you could within limits, did it, and Tony agreed it worked perfectly. The circular fuse was planned for mild pressurization.
Hell, the perfect bonding of the Lockheed patent process with spruce laminae would have handled it easily. There are also drawings of the planned Alcor C6-2, which would have packaged 2 of the proposed Menasco V-12's in place of the I6's.
The C6-1 exceeded 400 MPH in the power dive from which it recovered and flew graceful circles over Oakland Bay–without its witless pilots! So, the uprated performance with V-12's would have been incredible. In mid-1942, Lockheed introduced the C-60 variant of the "Lodestar".
Designed specifically for military use, the C-60 was used as a troop and cargo carrier, flew anti-submarine patrols, and performed Search and Rescue duties. A total of 21 more C-60 and 325 C-60A were delivered. One of the last was the C-60B with an experimental de-icing system with hot air.
The only aircraft model 18-10 with engines R-1830-53 with a power of 1200 hp. (895 kW) and 11 passenger seats was purchased in 1942 under the designation C-66 as VIP transport for the president of Brazil.
Expressing irritation with failure to equip transport planes with litter supports, the AAF Directorate of Military Requirements called upon the Materiel Command for a report. In reply that Command summarized the situation. All C-47s were completely equipped with litter supports during production.

While a shortage of critical materials had prevented installation in the first twenty-four C-46s delivered, all others would come equipped. Beginning in December 1942, all C-53s would be provided with litter brackets by manufacturers. Meanwhile, the Air Forces would install them in 200 planes of that type already delivered.
Beginning in January 1943, supports for ten litters would be placed in each C-60. Finally, all new types of transport would be equipped with litter supports when deliveries began. Interest of US military to "Lodestar" manifested itself for the first time in 1940, when the US Navy ordered one XR5O-1 and two R5O-1.
Similar aircraft were delivered to the US Coast Guard. They were equipped with Wright R-1870 engines. 12 R5O-4, 41 R5O-5 and 35 R5O-6 were built. The first two options were, respectively, a 4-7-seat administrative and 12-14-passenger passenger transport aircraft.
The third option was an 18-seat military transport aircraft used by the Marine Corps for parachuting operations. Equipped with engines Pratt & Whitney R-1830, one R5O-2 and three R5O-3 were built for the US Navy. After the war, many military Lodestars were declared surplus and sold to private operators for use as cargo or executive transports.
In 1957, the first fire jump for the California Smokejumpers was made out of a Lockheed Lodestar. The Lockheed Lodestar was powered by two 9-cylinder radial air-cooled engines providing a top cruise speed of 207 knots and a range of 1650 miles.
Originally designed for commercial flights, the Lodestar was frequently flown by the Air Force in the 1940s. After the war, the Lodestar returned to civilian service and eventually found its way into the Smokejumper program. The C-6-1 (registered as NX15544) was first flown on 6 March 1938. On a test flight over San Francisco Bay on 27 June 1938, the C-6-1 went out of control during a high-speed dive.
The dive test was instigated by the pilot and not part of the flight schedule. Unable to regain control, the pilot and observer bailed out, leaving the sleek C-6-1 to crash into the bay. The aircraft was insured, but the funds were only sufficient to pay off Alcor's debts.
With no capitol, Allan closed out Alcor. Allan continued to be involved in aviation for the rest of his life, but he did not build any further aircraft of his own design. Over the next few years, the Duo-4 was slowly repaired and modified.
The four-cylinder Pirate engines were replaced by six-cylinder Menasco B6S Buccaneer engines. The supercharged, 230 hp (171 kW) Buccaneers were in-line, air-cooled engines and turned 7 ft 6 in metal propellers. After the modifications, the aircraft was renamed the Duo-6 (some sources refer to it as the Loughead Alcor).
It flew again in early 1934. The Model 18 was developed because of problems with its predecessor, the Model 14 Super Electra (designated PBO and R4O in USN service). The first commercial operator of the Model 14 was Northwest Airlines which purchased eleven aircraft.
Three of these aircraft crashed between May 1938 and January 1939 causing the flying public to lose confidence in the aircraft and Northwest returned the Model 14s to Lockheed and purchased the slower Douglas DC-3 (R4D in USN service) in March 1939. During the same

period, five Model 14s crashed outside the U.S., one each in Canada, England and the Netherlands and two in Romania. Recognizing that it had a big problem, Lockheed began work on a replacement for the Model 14.
Even though the Duo-4 and Duo-6 were built under the Lockheed Brothers Aircraft Corporation name, they are often referred to as the Alcor Duo-4 and Alcor Duo-6. In addition, the Alcor C-6-1 is often incorrectly referred to as the Lockheed Alcor.
The Lockheed Model 18 Lodestar first flew in September 1939 [1940?], the Model 18 was originally designed as a successor to the Lockheed Model 14 and the earlier Model 10 Electra. The Army began ordering military versions of the Model 18 in May 1941. The Lodestar was offered with the Pratt & Whitney Hornet, Twin Wasp or Wright Cyclone engines and with various interior configurations.
Depending upon engines and interior configuration, these transports were given C-56, C-57, C-59, C-60 or C-66 basic type designations. The Duo-4 and Duo-6 had a 42 ft (12.80 m) wingspan and were 28 ft 6 in (8.69 m) in length.
The Duo-4 had an empty weight of 2,265 lb (1,027 kg). The aircraft had a maximum speed of 140 mph (225 km/h) and a landing speed of 47 mph (76 km/h). The Duo-6 had an empty weight of 2,885 lb (1,309 kg) and a gross weight of 5,090 lb (2,309 kg).
The aircraft had a max speed of 183 mph (295 km/h), a cruise speed of 157 mph (253 km/h), and a landing speed of 57 mph (92 km/h). The service ceiling was 18,500 ft (5,639 m) and its range was 660 mi (1,062 km).
The single engine performance of the Duo-6 was a max speed of 125 mph (201 km/h), a cruise speed of 100 mph (161 km/h), and a ceiling of 6,400 ft (1,951 m). The Junior Transport had a wingspan of 49 ft (14.94 m) and a length of 31 ft 8 in (9.65 m).
The aircraft had an empty weight of 4,141 lb (1,878 kg) and a gross weight of 6,200 lb (2,812 kg). The aircraft had a max speed of 211 mph (340 km/h) at 5,500 ft (1,676 m) and a cruise speed of 190 mph (306 km/h) at 5,500 ft (1,676 m) and 200 mph (322 km/h
) at 10,000 ft (3,048 m). The service ceiling was 24,000 ft (7,315 m) and its range was 835 mi (1,344 km). On one engine, the C-6-1 had a top speed of 147 mph (237 km/h), could cruise at 129 mph (208 km/h), and had a ceiling of 12,600 ft (3,840 m).
Since its inception, the C-5 has been a critical instrument of national policy. From the defense of Israel in the Yom Kippur war, to the air bridge supporting coalition forces in Desert Storm, the C-5 delivers unmatched capability to carry enormous loads over global distances.
In late 1941, when America entered the war, all "Lodestars" flying with the United States military were former airliners conscripted into service. These aircraft received different numerical designations depending on engine type. Most of the aircraft were removed from the US domestic service by December 1941, when they received a designation of a series of C-56: respectively, one C-56A, 13C-56B, 12C-56C, seven C-56D and two C

-56E. A total of 10 Model 18-07 and 15 Model 18-56 were designated respectively C-59 and C-60. The US Army Air Corps ordered one aircraft with Wright R-1820-29 engines in May 1941 under the designation C-56.
It was a military version of the Civil Model 18-50. After some time, three aircraft were ordered Model 18-14 with engines Pratt & Whitney R-1830-53. In addition, orders for seven and three cars were made. Accordingly, all 13 vehicles were designated as C-57.
The requisitioned civilian aircraft received the designation C-57A, seven military transport aircraft were known as the C-57B, and three of the latest C-60A aircraft were converted to Pratt & Whitney R-1830-43 star engines and designated C-57C
. One of these three aircraft was the C-57D, later equipped with R-1830-92 engines. I had understood that the Alcor engines (there is a drawing I have somewhere) were canted out 6 deg's each, included angle = 12 deg's.
That looks to be more extreme than reality. I like the 3.5 deg's/each better – don't know… In response to an escalating number of transport aircraft crashes in the mid-1940s, in the 1950s researchers at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory undertook a decade-long investigation into a number of issues surrounding low-altitude aircraft
crashes. The tests were conducted at the Ravenna Arsenal, approximately 60 miles south of the Lewis laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. The aircraft were excess military transports from World War II. The nine-crash initial phase of testing used Lockheed C-56 Lodestar and C-82 transport aircraft to identify potential ignition sources and analyze the spread of flammable materials.
@media only screen and (min-device-width : 320px) and (max-device-width : 480px) { #ga-ad {display: none;} } In 1929, the Lockheed Aircraft Corporation was bought by the Detroit Aircraft Corporation. Lockheed's founder, Allan H. Loughead (phonetically pronounced Lockheed) was unhappy with the acquisition and had voted against it.
Allan left and formed a new company in 1930 with his brother Malcolm. The pair had worked together in aviation before pursuing separate interests in the 1920s. The new company was known as the Lockheed Brothers Aircraft Corporation.
The Lockheed Model 14 Super Electra, and the Model 18 Lodestar proved to be extremely capable planes with among the best cruising speeds, ranges and altitude performance, besting that of its rival, the Douglas DC-3. The U.S.
Congress passed the Civil Aeronautics Act of 1938, which created the Civil Aeronautics Board, and in March 1939, National Airlines was issued its original certificate of convenience and necessity authorizing the carriage of mail, passengers, and property over its system.
The airline received the first of its 14-passenger Lockheed Lodestars in November 1940. During its delivery the plane set a transcontinental record of 9 hours and 29 minutes, which held for more than 15 years. Hi Bill, Great to run across your footprints and fine work here, after Reno.
The work you have done with the Olympic Duo cum Alcor is excellent, and also great to see Pancho Barnes with the Duo. Turns out Dad retained her to fly tests at Muroc of the Vega 5c, last and most upgraded version.
Allan Loughead officially changed his name to Allan Lockheed in February 1934. Also in 1934, the Lockheed Brothers Aircraft Corporation went out of business, but Allan continued with the Duo-6. In May 1934, one propeller was removed to demonstrate the Duo-6's single engine performance.
At Mines Field (now Los Angeles International Airport), the Duo-6 took off in 1,200 ft (366 m) and reached 130 mph (209 km/h) on just one engine. Reportedly, with one engine shut down, the aircraft handled with little yaw, much like a single-engine plane.
In May, Allan flew the Duo-6 back east to demonstrate it to the Navy and Army. However, nothing came from this exposure.
c 5 aircraft model, c 126 aircraft, c 46 aircraft models, c6 cargo plane, air force c5a galaxy, c6 jet, md 83 aircraft seating, nakajima c6n1 saiun myrt